Heating your home is an inevitable activity every winter season. The cheapest way to heat your home is through a space heater. Other cost-effective methods include standard air-source heat pumps, geothermal heat pumps, gas furnaces, ductless mini-split heat pumps, and gas boilers.
One readily apparent thing is that the above-mentioned heating systems work differently, which you can infer from their names. These heat pumps vary in their capabilities and their market value as well. However, they’re the cheapest of the bunch, so you’ll save money. Still, knowing these differences is crucial for every homeowner who wants to install a heating unit in their home.
As you read on, you’ll know how each efficient heating unit functions to generate warm air for the home.
Standard Air-Source Heat Pumps
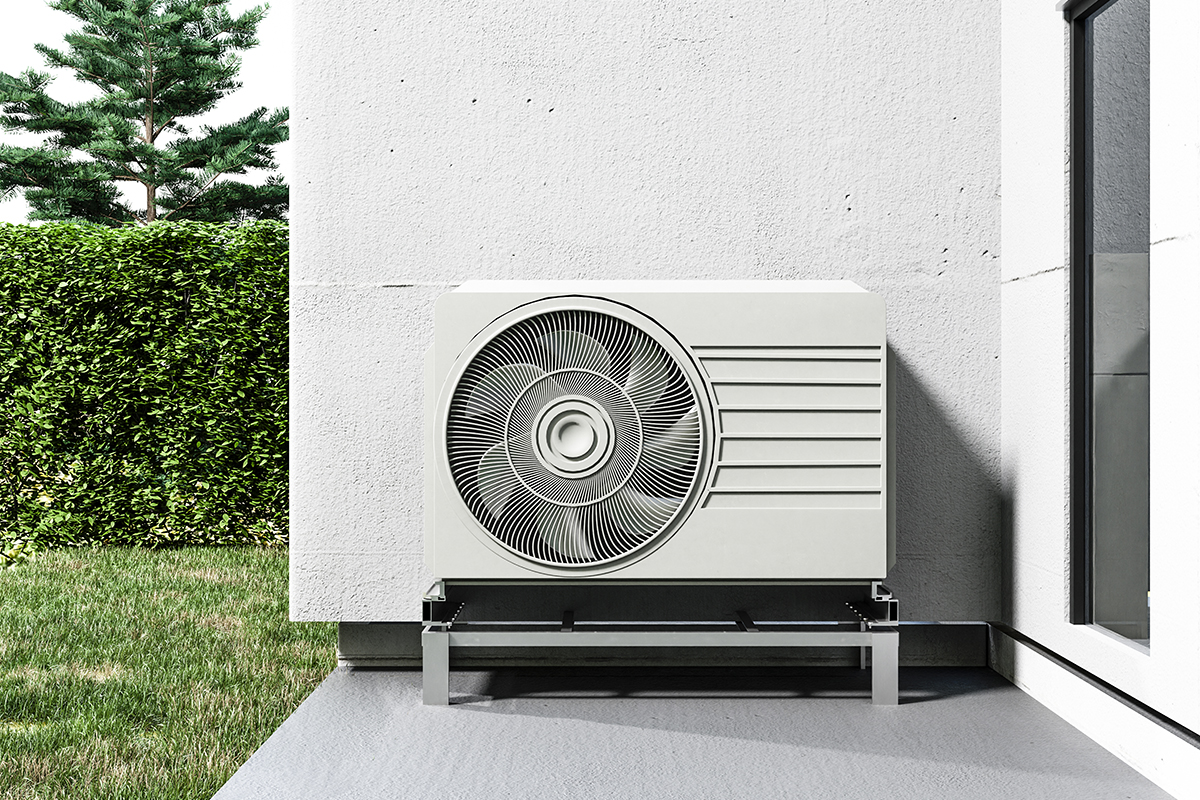

This heat pump is the most popular kind of heating unit in the U.S. Its design and functionality closely resemble central air conditioners. However, they differ from these systems because they generate both cool and warm air for the home.
The Components of this Heating System
This heater is comprised of all the major components that also make up a central air conditioning system, including:
- Air handler – the indoor unit
- Condenser – the outdoor unit
- Condensing coils
- Compressor
- Evaporator coils
- Thermal expansion valve
- Refrigerant lines
- Blower
This heater system also features a reversing valve which ensures the refrigerant flows in alternating directions. This is how this heater swaps between cooling and heating modes.
How do Standard Air-Source Heat Pumps Work?
This heating system utilizes the vapor-compression refrigeration cycle to cool and heat your home. This heat pump is a split system because it comprises an outdoor and indoor unit that swaps the refrigerant with each other to cool or warm the home.
The heating unit moves the compressed refrigerant at varying pressures and temperatures throughout the system’s significant components to keep the entire home warm. This heat pump heats your home by using a low-pressure and cool refrigerant to absorb heat from the cold air outside your home.
After the refrigerant becomes warm, the heat pump compresses it and pumps it into the indoor air handler to generate hot air for the home and move it throughout the ductwork.
How Much Does It Cost?
Air-source heating units can cost as low as $10k and as high as $20k, including installation charges. The price difference is based on certain factors, such as the brand and model of the heater, its size, ease of installation, and energy efficiency.
As for the running heating costs, the money can range between $550 and $1,200 yearly. Your operating costs or heating bill will vary depending on factors such as:
- The setpoint of your smart thermostat
- The heat pump’s efficiency
- Outdoor temperatures
- The size of your heat pump
- The insulation of your home
- The size of your home
- Your power bill
Another similarity this heating system shares with the geothermal heat pump are the possibility of refrigerant leaks. This can have a negative impact on human health and the environment. However, this heat pump differs from geothermal heat pumps as it costs less to install because it doesn’t require excavation work.
The Pros and Cons of This Heat Pump
The pros of this system include:
- Dual capability – it can either cool or heat the home.
- There’s no risk of carbon monoxide leaks.
- The initial purchase cost is considered fair since the system works as a cooler and heater.
- This heating system is very energy efficient.
- The system cools or heats the home via ductwork.
The cons of this system include:
- The standard heat pump may need to be supplemented by an energy-efficient space heater during the peak of the winter season. The standard heat pump will create heat efficiently during very cold weather conditions.
- Its upfront costs are higher than heating options such as the gas furnace.
- There’s little possibility of refrigerant leaks.
- Compared to gas furnaces, standard heat pumps cost more to maintain.
Geothermal Heat Pumps

The geothermal system is regarded as arguably the most efficient heating option that you can utilize to heat your home. The U.S Environmental Protection Agency stated that geothermal heat pumps could lessen one’s energy costs by virtually 50% when compared to heating units such as gas furnaces or gas boilers.
One might ask how efficient geothermal heating is. Geothermal systems, also called ground-source heat pumps, are highly efficient because they transfer heat from the ground to the home instead of creating it.
The average geothermal heat pump requires just about 1 BTU of energy to transfer 4 BTUs from the ground to your home. Mathematically, this translates to an efficiency percentage of 400%. Insane, right?
Geothermal Heat Pump Components
This heating system works similarly to the standard heat pumps because they both utilize vapor-compression to transfer heat. Its components are also very similar to those of the air-source heating systems. They include:
- Condenser
- Compressor
- Thermal expansion valve
- Refrigerant lines
- Indoor blower
- Evaporator
- Reversing valve
How do Geothermal Heat Pumps work?
This heating system functions by drawing heat from the earth and transferring it to your home to keep it warm. These heating systems draw this heat from the ground using underground piping containing refrigerant that will capture heat.
The compressor pushes the refrigerant via these underground pipes, increasing the pressure of pumping to increase its temperature as well. These refrigerant pipes work like a condenser while underground. Once the refrigerant traps the heat from the ground, it will flow to the indoor coils in your home.
Once it gets to your home, the blower pushes air through the evaporator coils. This triggers heat transfer from the refrigerant to the air and circulates it through the ductwork to reach the entire house.
Usually, the refrigerant remains within the geothermal pump. However, if a refrigerant leaks, it will enter the atmosphere. R-134a, a common refrigerant in residential heating systems, is a hydrofluorocarbon. This means if it leaks into the atmosphere, it will deplete ozone.
Admittedly, its ozone depletion impact is small and even smaller in terms of its potential to trigger global warming. However, it still negatively impacts the environment if leaked.
How Much does it Cost?
Geothermal heat pumps cost more than standard heat pumps. They range from $18k to $45k, depending on the location for installation and size. A significant reason why the cost of this heating system is higher than the standard heat pump is that it requires excavation or digging of the ground to install the refrigerant pipes of the heating system underground.
The monthly heating bill for this heating system will range from $30 to $55. Depending on your local utility bills and location, the price will be higher or lower.
Geothermal Pros and Cons
The pros of the geothermal system include:
- Since you won’t be paying for drawing the heat from its primary heating source – the ground, this keeps your heating costs low, helping you save money.
- This system can keep your home cool during the summer season.
- It’s regarded as the most efficient heating system.
- No risk of carbon monoxide poisoning
- The system has high energy efficiency.
The cons of the geothermal system include:
- There’s a risk of refrigerant leaks.
- The installation cost is higher and costs more than the standard heat pump.
- The repair cost is high.
- This heating system may require supplementary heating during extreme weather conditions to keep the house warm.
Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps
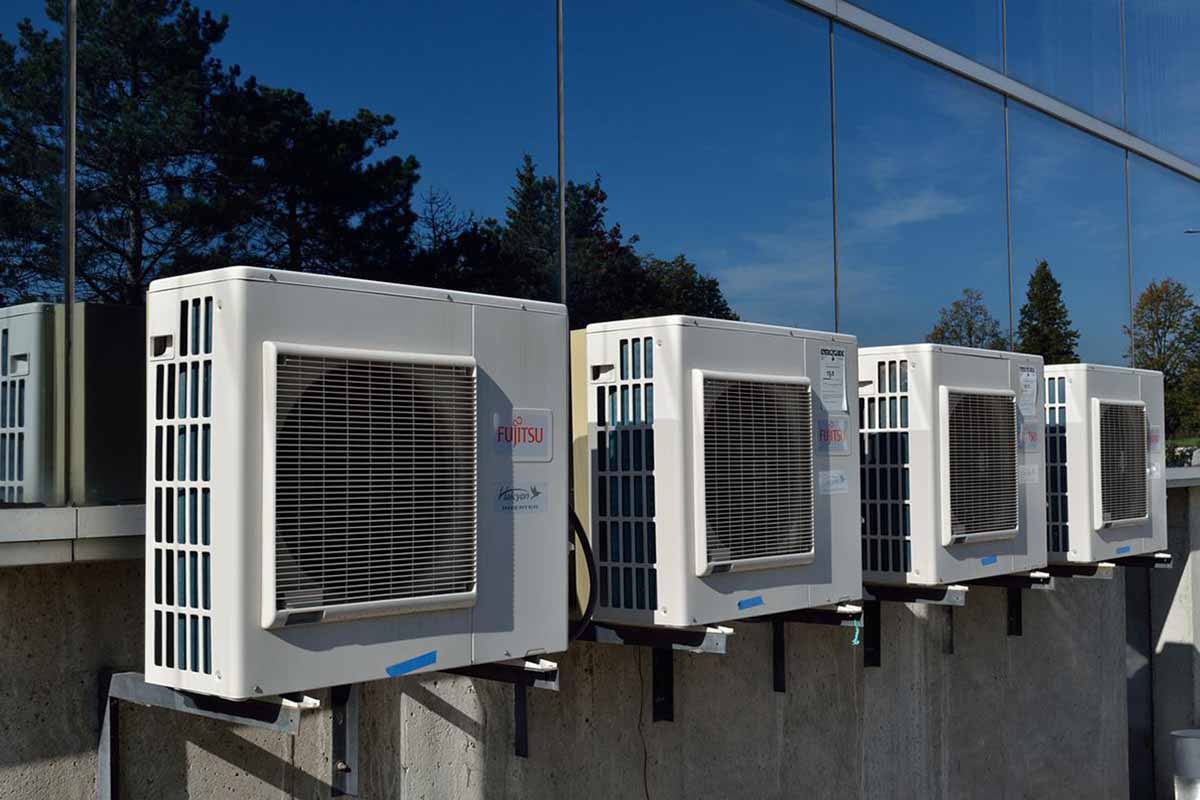

This is the mini version of the standard heat pump, which can only heat one room. It comprises an indoor unit and an outdoor unit. The latter component connects to the former, usually hanging on a home wall. The heating system also has wiring and refrigerant lines.
How do Ductless Mini-Split Units work?
These heating systems utilize vapor-compression and the well-known parts of a standard heat pump to warm your home, but it does this with less capacity. Unlike the standard version, mini-split heating units don’t connect to the ductwork of your home. These heating systems are among the most energy-efficient heating units because losing heat via ductwork won’t happen.
However, when the temperature outside gets too cold, possibly around a range of 30°F, this heating system will not be very efficient in keeping the home warm. The reason for the decline in efficiency is that the air will have less heat. This will take the heat pump longer to get heat from outdoors.
How Much does it Cost?
The cost of these heating units ranges from $3k to $5k for a single zone. Extra zones will cost around $1.5k to $2.5k, respectively. A single outdoor unit can be linked to several indoor units to heat rooms in the home. This saves you extra bucks because you don’t have to buy additional outdoor units for each room in the home.
According to the U.S Department of Energy, these heating systems will cost you a pocket-friendly electric bill between $200 and $325 annually for each zone.
Many factors will determine the heating bill of your heating system including:
- Energy efficiency
- Size
- The setpoint of your programmable thermostat
- The size and insulation of the zones
- Outdoor temperatures
- Utility bill
Pros and Cons of Ductless Mini-Split Heating Systems
The pros of this heating system include;
- Its upfront cost is lower.
- It doesn’t require ductwork.
- It’s very energy-efficient and incurs low heating costs.
- There’s no risk of carbon monoxide leaks, which means no risk of air pollution.
- There’s separate temperature control for the respective zones.
The cons of this heating system include:
- It consumes wall space.
- It may require extra heating via space heaters when it’s freezing.
- It can only heat a single room.
- Its efficiency declines in freezing temperatures.
- There’s a small risk of refrigerant leaks.
Space Heaters

This heating system provides ample heating for the home and also cools the home during the summer, taking some work off your HVAC systems.
How do Space Heaters Function?
They convert electricity into heat to warm the home during the winter season. How they work depends on the type of space heaters. They include:
- Convection Heaters: This type of space heater uses electrical energy to heat metallic coils. When air blows across these heated coils, it transfers heat to the home.
- Oil-Filled Heaters: This type of heater uses electricity to heat the metal that warms its oil. It then transfers this heat to the room.
- Infrared Heater: This type generates radiant heat. Instead of transferring the heat to the air, it directly transfers it to objects in the room.
- Propane Heaters: This type burns propane gas to generate heat for the home.
How Much does it Cost?
The space heater is the cheapest way to heat your home. The upfront cost for infrared heaters ranges between $50 and 300. Oil-filled heaters cost between $70 and $130. Convection heaters go for any price between $30 and $80. Last but not least, propane heaters costs between $50 and $175. The exact price tag depends on its capacity.
Pros and Cons of Space Heaters
The pros of the space heater include:
- It’s portable.
- It heats the room quickly.
- It reduces your home’s energy usage.
- It’s easy to provide heat for your rooms.
The cons of the space heater include:
- It can only heat a small portion of your home.
- There’s a high risk of a fire hazard. For instance, when you put a cloth over the heater.
- It consumes space on your floor.
- Depending on the model and brand, it can be noisy.
Gas Boilers
You can also call them hot water heaters. Before gas furnaces stole the spotlight, these heating systems were one of the most common heating methods in homes. It was second only to wood-burning stoves in popularity. They are less popular because of their relatively higher upfront costs.
Gas boilers have electric models known as electric boilers or electric heaters. However, just like electric furnaces, they are less cost-effective than their natural gas-burning counterparts. Their maximum efficiency is 96% AFUE.
How do Gas Boilers Work?
It works just like gas furnaces. They both burn natural gas, one of the most common fossil fuels, to generate heat for the home. But these efficient heating systems differ in how they exchange heat with the air inside the house. This heating system utilizes a natural gas burner to heat water to extremely high temperatures, surpassing the 100°C.
This natural-gas heating system has a pump that moves a mixture of the steam and hot water across your home to cast iron radiators, baseboard radiators, or a radiant heat flooring system. They provide an even distribution of heat in the house, producing hot air that’s less dry than gas furnaces.
How Much does it Cost?
On average, the cost of a gas boiler ranges between $2.5k to $10k. This includes installation charges because the heating lines and radiators will require setting up. The following factors determine the price of a gas boiler:
- Energy-efficiency
- Capacity
- Brand and model
- Cost of labor in your location
The yearly heating bills for a gas boiler range from $500 to $1,800, which is on the high side compared to other heating options. The operating cost varies depending on the efficiency and size of your system.
Gas Furnaces

This heating system burns propane or natural gas on a burner. Above this burner, there’s a heat exchanger which gathers the heat generated from the burning process. The blower draws in the cold air from the house and channels or across the heat exchanger. This triggers the cold air to retain the heat from the heat exchangers.
Afterward, it passes through the ductwork of your home and goes to the supply vents of all the rooms in your home. This process repeats itself until the thermostat in your home reaches its setpoint. Simultaneously, the burnt gas (containing carbon monoxide) exits from the home through the furnace’s chimney.
A gas furnace is a great heating unit many homeowners can invest in for its low operating cost. If you live in a colder climate, get one with 90% Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) or heat percentage generated per dollar of petrol consumed. For areas with milder weather, models at 80% can serve you just fine.
How Much does it Cost?
Gas furnaces have an average upfront cost that ranges from $750 to $1,200. The cost of installation is higher as it ranges from $1,750 to $2,400. This total cost ranges from $2,250 to $3,600 for both purchase and installation.
If your gas furnace malfunctions, you can easily find a repair company to get it back in working condition. Experts like Air Makers help homeowners make the most out of their units through reliable repair services.
Speaking of which, rates for repairs vary between places. In the US, they usually cost between USD$300 to USD$1,200. The nature and extent of the heating unit’s problem will also affect costs. So, it’s a good idea to ask for quotes and compare rates between companies for the best value for your money.
How about the energy consumption rate? A gas-fired, forced-air furnace requires little power to warm your home. Most gas heat furnaces utilize electricity below 600 watts, which is about less than 50% of a 15-ampere power circuit.
The annual heating costs for a gas furnace range between $600 and $2,000. This cost vary based on several factors, including:
- The thermostat’s setpoint
- Outdoor temperatures
- Natural gas prices in your area of residence
- The length of the winter season
- Capacity
- Fuel efficiency
Pros and Cons of Gas Furnaces
The pros of this heating system include:
- The system is very energy-efficient.
- Compared to heat pumps, the energy bill is low.
- Repairs and maintenance don’t cost much.
- Ample heating capacity
The cons of this heating system include:
- It makes more noise than a heat pump.
- The direct usage of fossil fuels isn’t good for the environment.
- There’s a risk of carbon monoxide leakage.
Proper Heating Within Your Reach
Heating your home year-round shouldn’t have to cost a fortune. Whether you choose a heat pump, space heater, boiler, or gas furnace, you’re set so long as you work with professionals for installations, maintenance, and repairs. Find the one that works best for you today.











